2021
-
 Ultracompact fluorescence smartphone attachment using built-in optics for protoporphyrin-IX quantification in skinHunt, Brady, Streeter, Samuel S, Ruiz, Alberto J, Chapman, M Shane, and Pogue, Brian WBiomedical Optics Express 2021
Ultracompact fluorescence smartphone attachment using built-in optics for protoporphyrin-IX quantification in skinHunt, Brady, Streeter, Samuel S, Ruiz, Alberto J, Chapman, M Shane, and Pogue, Brian WBiomedical Optics Express 2021Smartphone-based fluorescence imaging systems have the potential to provide convenient quantitative image guidance at the point of care. However, common approaches have required the addition of complex optical attachments, which reduce translation potential. In this study, a simple clip-on attachment appropriate for fluorescence imaging of protoporphyrin-IX (PpIX) in skin was designed using the built-in light source and ultrawide camera sensor of a smartphone. Software control for image acquisition and quantitative analysis was developed using the 10-bit video capability of the phone. Optical performance was characterized using PpIX in liquid tissue phantoms and endogenously produced PpIX in mice and human skin. The proposed system achieves a very compact form factor (<30 cm3) and can be readily fabricated using widely available low-cost materials. The limit of detection of PpIX in optical phantoms was <10 nM, with good signal linearity from 10 to 1000 nM (R2 >0.99). Both murine and human skin imaging verified that in vivo PpIX fluorescence was detected within 1 hour of applying aminolevulinic acid (ALA) gel. This ultracompact handheld system for quantification of PpIX in skin is well-suited for dermatology clinical workflows.
-
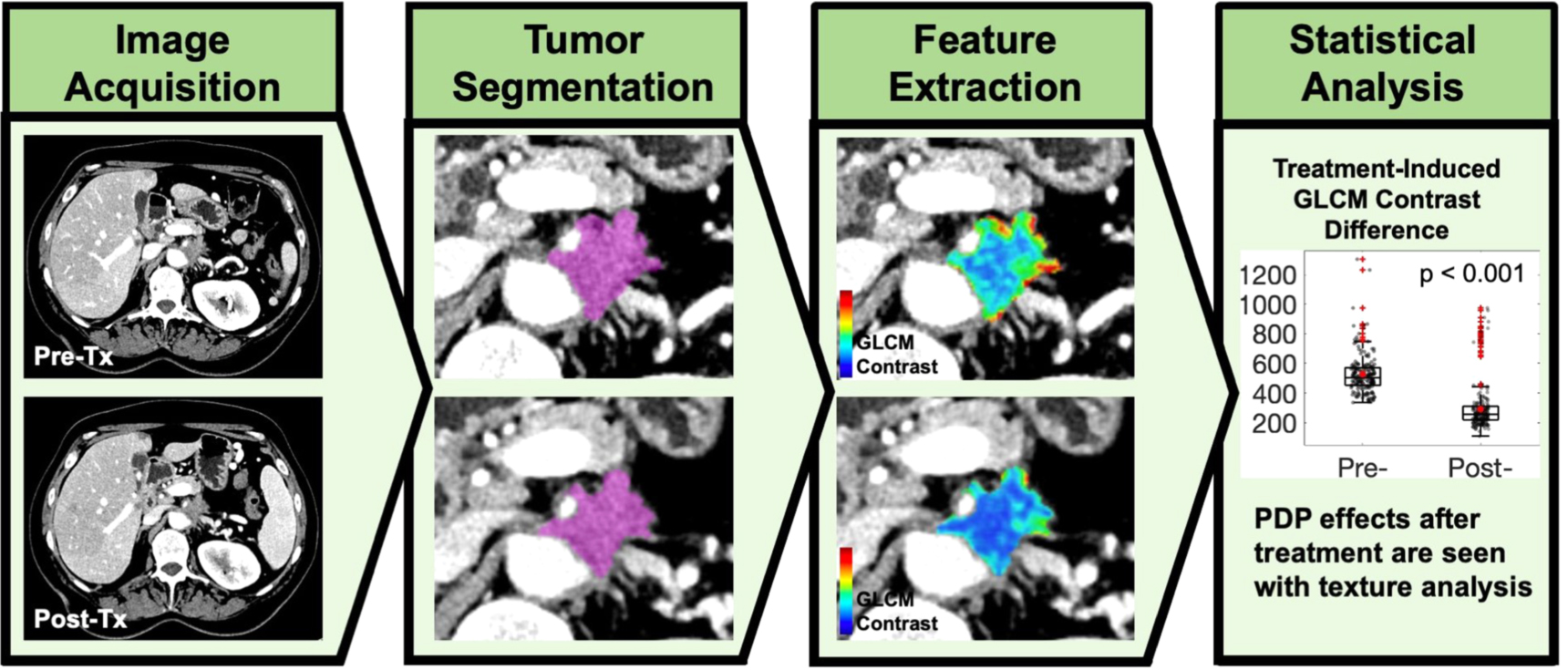
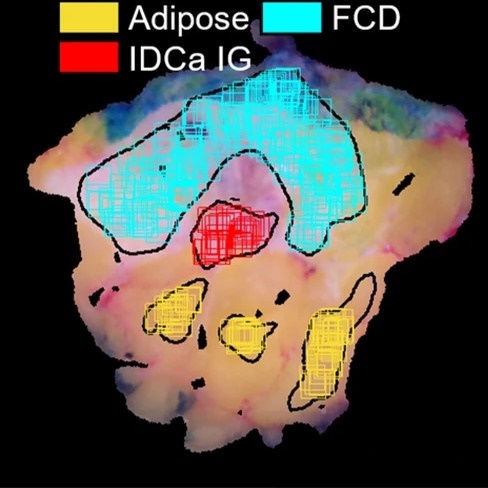 Developing diagnostic assessment of breast lumpectomy tissues using radiomic and optical signaturesStreeter, Samuel S, Hunt, Brady, Zuurbier, Rebecca A, Wells, Wendy A, Paulsen, Keith D, and Pogue, Brian WScientific reports 2021
Developing diagnostic assessment of breast lumpectomy tissues using radiomic and optical signaturesStreeter, Samuel S, Hunt, Brady, Zuurbier, Rebecca A, Wells, Wendy A, Paulsen, Keith D, and Pogue, Brian WScientific reports 2021High positive margin rates in oncologic breast-conserving surgery are a pressing clinical problem. Volumetric X-ray scanning is emerging as a powerful ex vivo specimen imaging technique for analyzing resection margins, but X-rays lack contrast between non-malignant and malignant fibrous tissues. In this study, combined micro-CT and wide-field optical image radiomics were developed to classify malignancy of breast cancer tissues, demonstrating that X-ray/optical radiomics improve malignancy classification. Ninety-two standardized features were extracted from co-registered micro-CT and optical spatial frequency domain imaging samples extracted from 54 breast tumors exhibiting seven tissue subtypes confirmed by microscopic histological analysis. Multimodal feature sets improved classification performance versus micro-CT alone when adipose samples were included (AUC = 0.88 vs. 0.90; p-value = 3.65e−11) and excluded, focusing the classification task on exclusively non-malignant fibrous versus malignant tissues (AUC = 0.78 vs. 0.85; p-value = 9.33e−14). Extending the radiomics approach to high-dimensional optical data—termed “optomics” in this study—offers a promising optical image analysis technique for cancer detection.
-
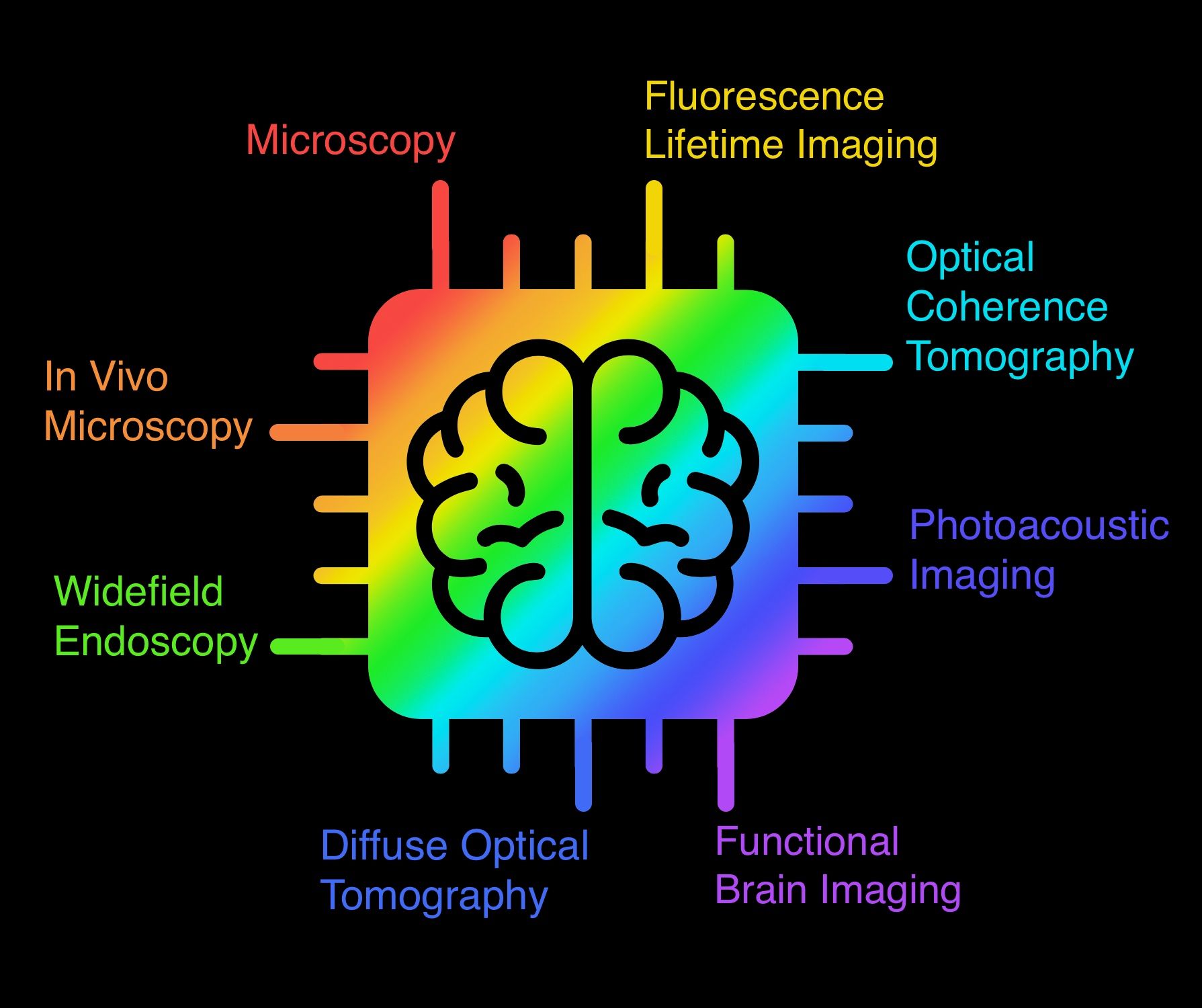 Deep learning in biomedical opticsTian, Lei, Hunt, Brady, Bell, Muyinatu A Lediju, Yi, Ji, Smith, Jason T, Ochoa, Marien, Intes, Xavier, and Durr, Nicholas JLasers in Surgery and Medicine 2021
Deep learning in biomedical opticsTian, Lei, Hunt, Brady, Bell, Muyinatu A Lediju, Yi, Ji, Smith, Jason T, Ochoa, Marien, Intes, Xavier, and Durr, Nicholas JLasers in Surgery and Medicine 2021This article reviews deep learning applications in biomedical optics with a particular emphasis on image formation. The review is organized by imaging domains within biomedical optics and includes microscopy, fluorescence lifetime imaging, in vivo microscopy, widefield endoscopy, optical coherence tomography, photoacoustic imaging, diffuse tomography, and functional optical brain imaging. For each of these domains, we summarize how deep learning has been applied and highlight methods by which deep learning can enable new capabilities for optics in medicine. Challenges and opportunities to improve translation and adoption of deep learning in biomedical optics are also summarized.
-
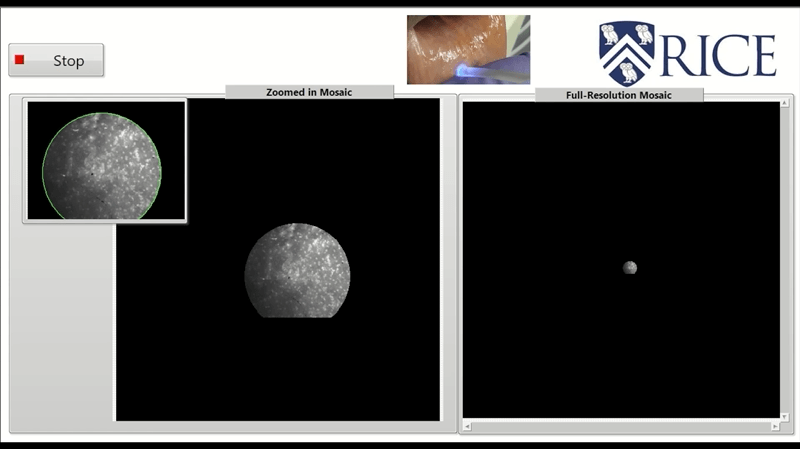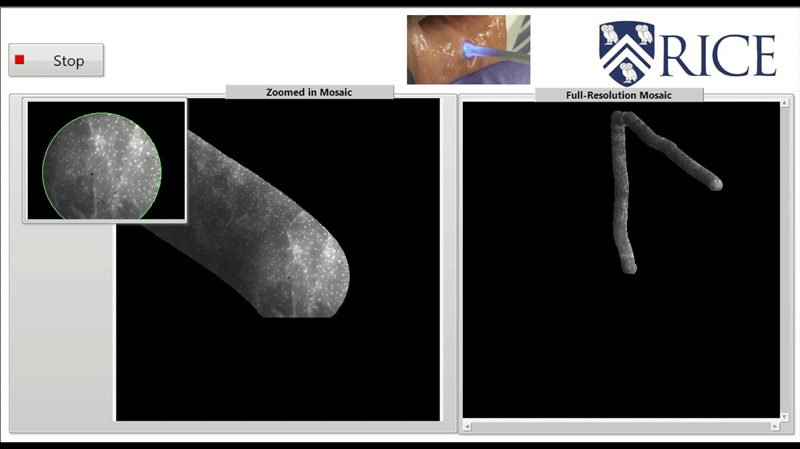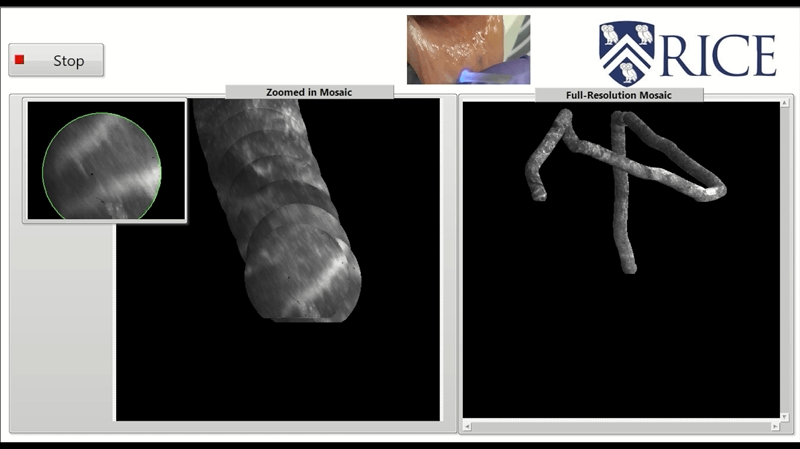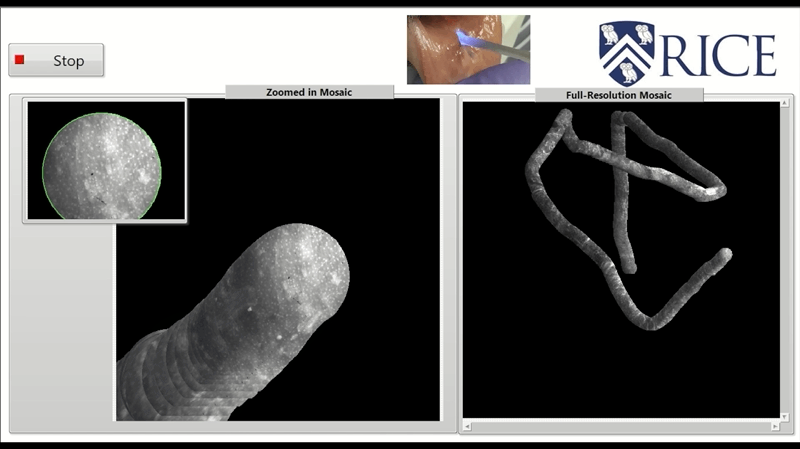 High frame rate video mosaicking microendoscope to image large regions of intact tissue with subcellular resolutionHunt, Brady, Coole, Jackson, Brenes, David, Kortum, Alex, Mitbander, Ruchika, Vohra, Imran, Carns, Jennifer, Schwarz, Richard, and Richards-Kortum, RebeccaBiomedical Optics Express 2021
High frame rate video mosaicking microendoscope to image large regions of intact tissue with subcellular resolutionHunt, Brady, Coole, Jackson, Brenes, David, Kortum, Alex, Mitbander, Ruchika, Vohra, Imran, Carns, Jennifer, Schwarz, Richard, and Richards-Kortum, RebeccaBiomedical Optics Express 2021High-resolution microendoscopy (HRME) is a low-cost strategy to acquire images of intact tissue with subcellular resolution at frame rates ranging from 11 to 18 fps. Current HRME imaging strategies are limited by the small microendoscope field of view (∼0.5 mm2); multiple images must be acquired and reliably registered to assess large regions of clinical interest. Image mosaics have been assembled from co-registered frames of video acquired as a microendoscope is slowly moved across the tissue surface, but the slow frame rate of previous HRME systems made this approach impractical for acquiring quality mosaicked images from large regions of interest. Here, we present a novel video mosaicking microendoscope incorporating a high frame rate CMOS sensor and optical probe holder to enable high-speed, high quality interrogation of large tissue regions of interest. Microendoscopy videos acquired at >90 fps are assembled into an image mosaic. We assessed registration accuracy and image sharpness across the mosaic for images acquired with a handheld probe over a range of translational speeds. This high frame rate video mosaicking microendoscope enables in vivo probe translation at >15 millimeters per second while preserving high image quality and accurate mosaicking, increasing the size of the region of interest that can be interrogated at high resolution from 0.5 mm2 to >30 mm2. Real-time deployment of this high-frame rate system is demonstrated in vivo and source code made publicly available.
-
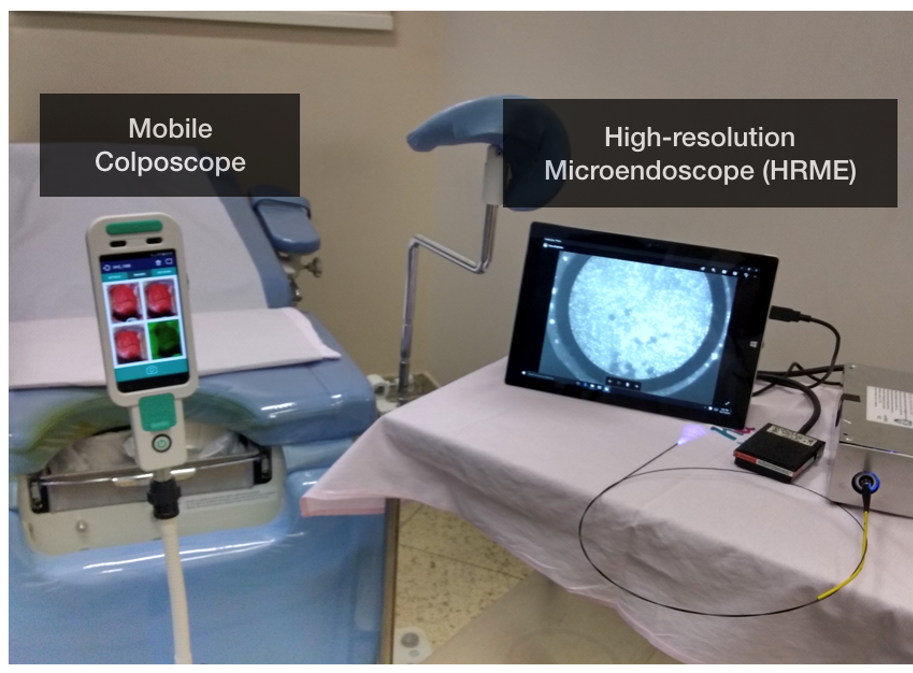 Cervical lesion assessment using real-time microendoscopy image analysis in Brazil: The CLARA studyHunt, Brady, Fregnani, José Humberto Tavares Guerreiro, Brenes, David, Schwarz, Richard A, Salcedo, Mila P, Possati-Resende, Júlio César, Antoniazzi, Márcio, Oliveira Fonseca, Bruno, Santana, Iara Viana Vidigal, Macêdo Matsushita, Graziela, and others,International journal of cancer 2021
Cervical lesion assessment using real-time microendoscopy image analysis in Brazil: The CLARA studyHunt, Brady, Fregnani, José Humberto Tavares Guerreiro, Brenes, David, Schwarz, Richard A, Salcedo, Mila P, Possati-Resende, Júlio César, Antoniazzi, Márcio, Oliveira Fonseca, Bruno, Santana, Iara Viana Vidigal, Macêdo Matsushita, Graziela, and others,International journal of cancer 2021We conducted a prospective evaluation of the diagnostic performance of high-resolution microendoscopy (HRME) to detect cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) in women with abnormal screening tests. Study participants underwent colposcopy, HRME and cervical biopsy. The prospective diagnostic performance of HRME using an automated morphologic image analysis algorithm was compared to that of colposcopy using histopathologic detection of CIN as the gold standard. To assess the potential to further improve performance of HRME image analysis, we also conducted a retrospective analysis assessing performance of a multi-task convolutional neural network to segment and classify HRME images. One thousand four hundred eighty-six subjects completed the study; 435 (29%) subjects had CIN Grade 2 or more severe (CIN2+) diagnosis. HRME with morphologic image analysis for detection of CIN Grade 3 or more severe diagnoses (CIN3+) was similarly sensitive (95.6% vs 96.2%, P = .81) and specific (56.6% vs 58.7%, P = .18) as colposcopy. HRME with morphologic image analysis for detection of CIN2+ was slightly less sensitive (91.7% vs 95.6%, P < .01) and specific (59.7% vs 63.4%, P = .02) than colposcopy. Images from 870 subjects were used to train a multi-task convolutional neural network-based algorithm and images from the remaining 616 were used to validate its performance. There were no significant differences in the sensitivity and specificity of HRME with neural network analysis vs colposcopy for detection of CIN2+ or CIN3+. Using a neural network-based algorithm, HRME has comparable sensitivity and specificity to colposcopy for detection of CIN2+. HRME could provide a low-cost, point-of-care alternative to colposcopy and biopsy in the prevention of cervical cancer.
-
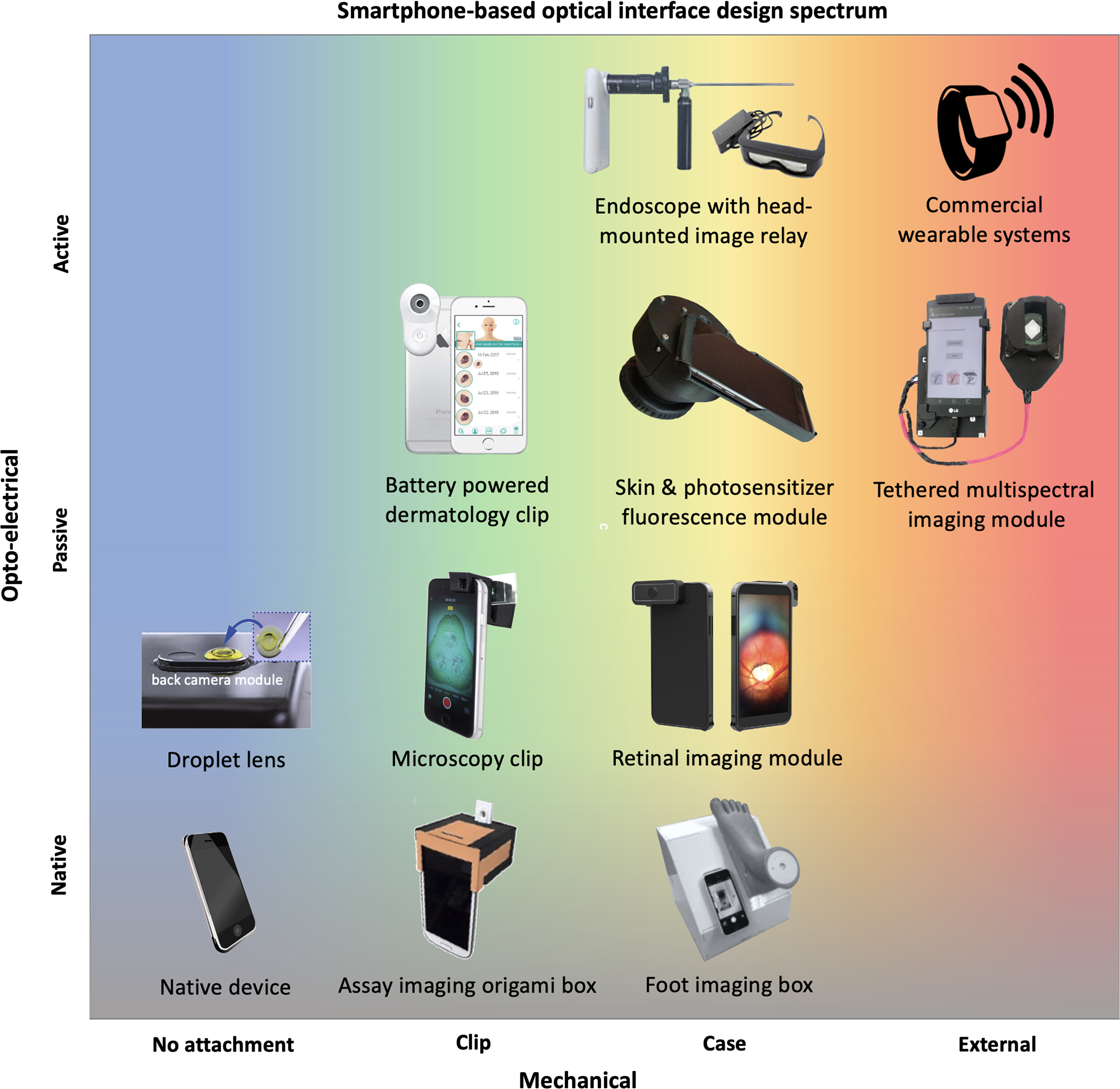 Smartphone-based imaging systems for medical applications: a critical reviewHunt, Brady, Ruiz, Alberto J, and Pogue, Brian WJournal of Biomedical Optics 2021
Smartphone-based imaging systems for medical applications: a critical reviewHunt, Brady, Ruiz, Alberto J, and Pogue, Brian WJournal of Biomedical Optics 2021Our review studies how smartphone-based imaging (SBI) systems are designed and tested for specialized applications in medicine and healthcare. An evaluation of current research studies is used to provide guidelines for improving the impact of these research advances. A holistic assessment of SBI systems must include interpretation of their value for intended clinical settings and how their implementations enable better workflow. A set of six guidelines are proposed to evaluate appropriateness of smartphone utilization in terms of clinical context, completeness, compactness, connectivity, cost, and claims. Ongoing work should prioritize realistic clinical assessments with quantitative and qualitative comparison to non-smartphone systems to clearly demonstrate the value of smartphone-based systems.
2020
-
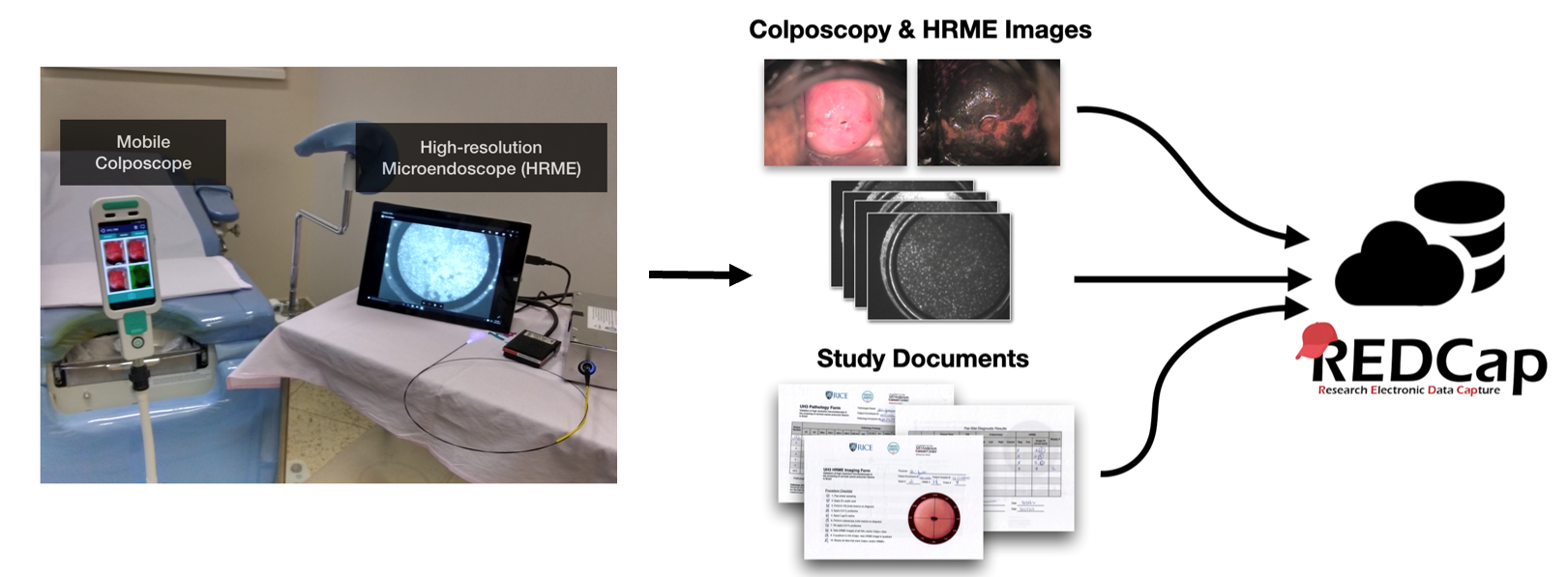 Diagnosing Cervical Neoplasia in Rural Brazil: Clinical Trial Outcomes and a Next-generation Point-of-care Imaging SystemHunt, Brady2020
Diagnosing Cervical Neoplasia in Rural Brazil: Clinical Trial Outcomes and a Next-generation Point-of-care Imaging SystemHunt, Brady2020This work contains a series of clinical studies conducted at a Brazilian cancer hospital to validate a low-cost, portable, high-resolution microendoscope (HRME) for real-time diagnostic evaluation of cervical lesions. Findings from these clinical studies led me to explore two approaches to further improve HRME: 1) improved image analysis algorithms and 2) improved optical instrumentation. In total, five studies are presented: three clinical studies and two technical studies. Taken altogether, these studies provide strong evidence for the potential of HRME to improve cervical cancer prevention in low-resource healthcare settings.
-
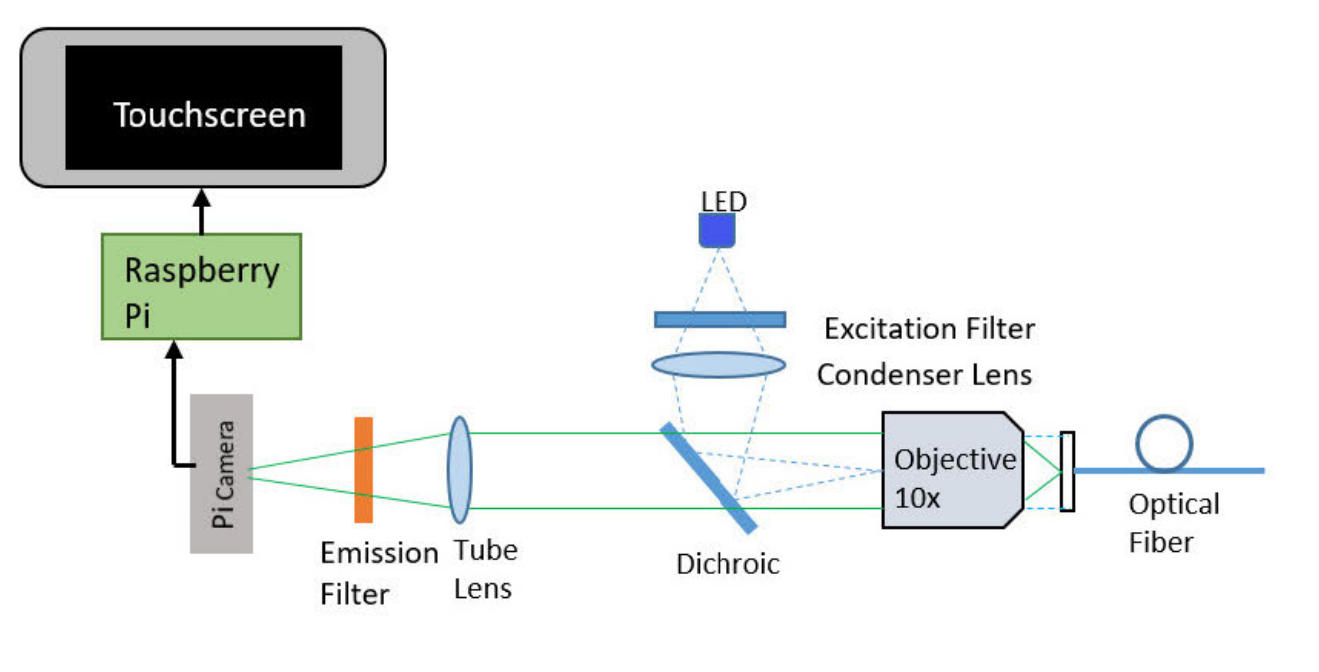 Development of low-cost point-of-care technologies for cervical cancer prevention based on a single-board computerParra, Sonia, Carranza, Eduardo, Coole, Jackson, Hunt, Brady, Smith, Chelsey, Keahey, Pelham, Maza, Mauricio, Schmeler, Kathleen, and Richards-Kortum, RebeccaIEEE journal of translational engineering in health and medicine 2020
Development of low-cost point-of-care technologies for cervical cancer prevention based on a single-board computerParra, Sonia, Carranza, Eduardo, Coole, Jackson, Hunt, Brady, Smith, Chelsey, Keahey, Pelham, Maza, Mauricio, Schmeler, Kathleen, and Richards-Kortum, RebeccaIEEE journal of translational engineering in health and medicine 2020Cervical cancer disproportionally affects women in low- and middle-income countries, in part due to the difficulty of implementing existing cervical cancer screening and diagnostic technologies in low-resource settings. Single-board computers offer a low-cost alternative to provide computational support for automated point-of-care technologies. Here we demonstrate two new devices for cervical cancer prevention that use a single-board computer: 1) a low-cost imaging system for real-time detection of cervical precancer and 2) a low-cost reader for real-time interpretation of lateral flow-based molecular tests to detect cervical cancer biomarkers. Using a Raspberry Pi computer to provide real-time image collection and processing, we developed: 1) a low-cost, portable high-resolution microendoscope system (PiHRME); and 2) a low-cost automatic lateral flow test reader (PiReader). The PiHRME acquired high-resolution (4.4 μm ) images of the cervix at half the cost of existing high-resolution microendoscope systems; image analysis algorithms based on convolutional neural networks were implemented to provide real-time image interpretation. The PiReader acquired and analyzed images of a point-of-care human papillomavirus (HPV) serology test with the same contrast and accuracy as a standard flatbed high-resolution scanner coupled to a laptop computer, for less than one-fifth of the cost. Raspberry Pi single-board computers provide a low-cost means to implement point-of-care tools with automatic image analysis. This work demonstrates the promise of single-board computers to develop and translate low-cost, point-of-care technologies for use in low-resource settings.
2019
-
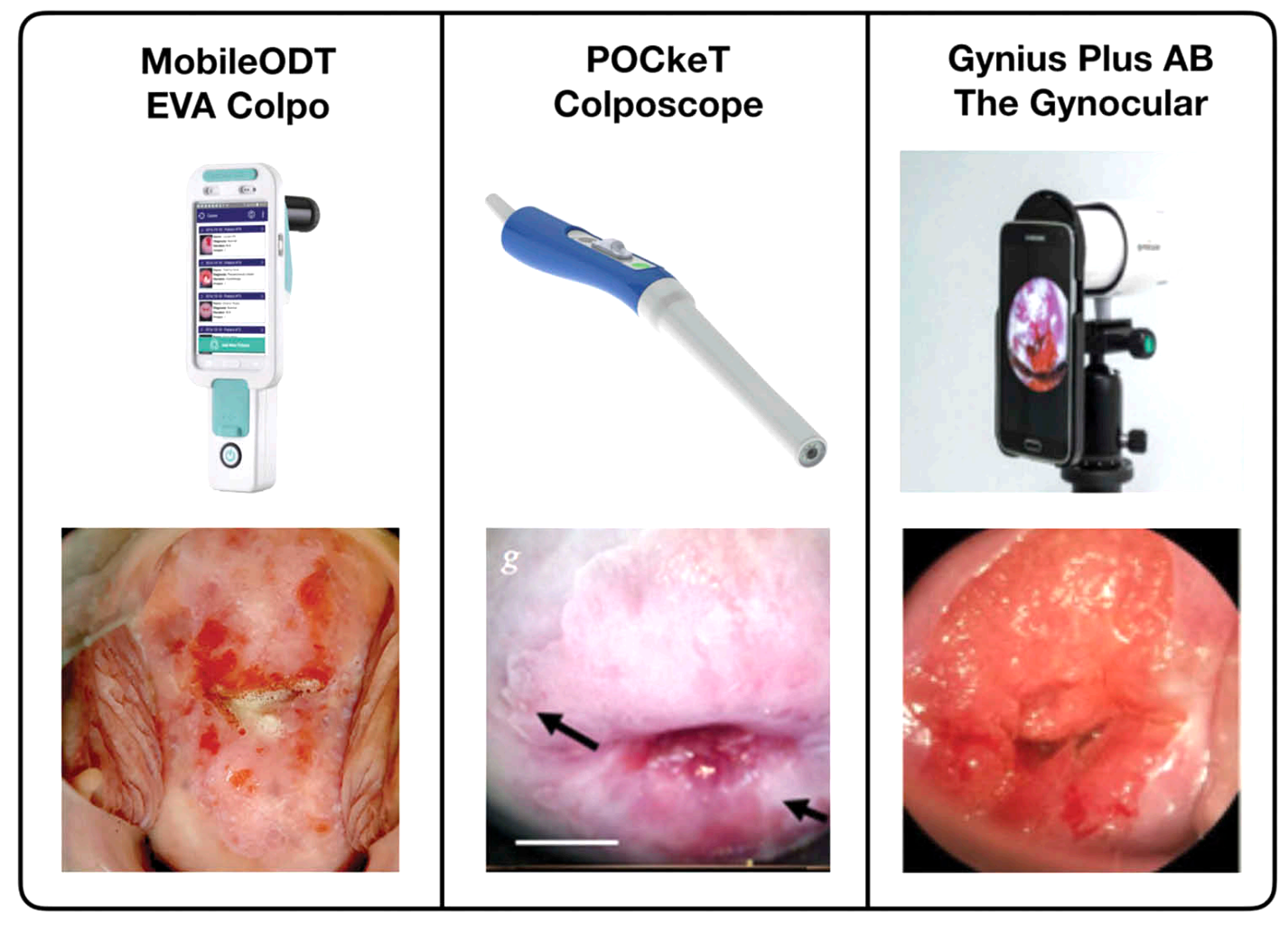 Advances in technologies for cervical cancer detection in low-resource settingsKundrod, Kathryn A, Smith, Chelsey A, Hunt, Brady, Schwarz, Richard A, Schmeler, Kathleen, and Richards-Kortum, RebeccaExpert review of molecular diagnostics 2019
Advances in technologies for cervical cancer detection in low-resource settingsKundrod, Kathryn A, Smith, Chelsey A, Hunt, Brady, Schwarz, Richard A, Schmeler, Kathleen, and Richards-Kortum, RebeccaExpert review of molecular diagnostics 2019Introduction: Cervical cancer mortality rates remain high in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) and other medically underserved areas due to challenges with implementation and sustainability of routine screening, accurate diagnosis, and early treatment of preinvasive lesions. Areas covered: In this review, we first discuss the standard of care for cervical cancer screening and diagnosis in high- and low-resource settings, biomarkers that correlate to cervical precancer and cancer, and needs for new tests. We review technologies for screening and diagnosis with a focus on tests that are already in use in LMICs or have the potential to be adapted for use in LMICs. Finally, we provide perspectives on the next five years of technology development for improved cervical cancer screening and diagnosis in LMICs. Expert opinion: Innovation toward improved molecular and imaging tests is needed to enable effective, affordable see-and-treat approaches to detect and treat cervical precancer in a single visit. Current molecular tests remain too complex and/or costly for widespread use. Especially with imaging tests, decision support may improve performance of new technologies.
2018
-
 Is proflavine exposure associated with disease progression in women with cervical dysplasia? A brief reportPantano, Naitielle, Hunt, Brady, Schwarz, Richard A, Parra, Sonia, Cherry, Katelin, Possati-Resende, Júlio César, Longatto-Filho, Adhemar, Fregnani, José Humberto Tavares Guerreiro, Castle, Philip E, Schmeler, Kathleen, and others,Photochemistry and photobiology 2018
Is proflavine exposure associated with disease progression in women with cervical dysplasia? A brief reportPantano, Naitielle, Hunt, Brady, Schwarz, Richard A, Parra, Sonia, Cherry, Katelin, Possati-Resende, Júlio César, Longatto-Filho, Adhemar, Fregnani, José Humberto Tavares Guerreiro, Castle, Philip E, Schmeler, Kathleen, and others,Photochemistry and photobiology 2018Proflavine is an acridine dye used with high-resolution microendoscopy for in vivo diagnostic evaluation of cervical epithelial cells. However, there are concerns that even short-term exposure of cervical tissue to dilute proflavine may increase cervical cancer risk. We performed a retrospective analysis of women referred for colposcopy to Barretos Cancer Hospital comparing the risk of cervical disease progression in those whose cervical tissue was (n = 232) or was not exposed (n = 160) to proflavine. Patients in both groups underwent treatment and follow-up based on histopathologic results and per the local standards of care. Progression of disease was evaluated by comparing histopathology from the initial visit to the worst subsequent histopathology result from all follow-up visits. Mean duration of follow-up was 18.7 and 20.1 months for the proflavine-exposed and controls groups, respectively. There were no significant differences in disease progression from normal/CIN1 to CIN2/3 or from any initial diagnosis to invasive cancer between the proflavine exposed and control groups overall. Risks of cervical dysplasia progression observed in this study are in agreement with those of the natural history of cervical cancer. Our results suggest that cervical exposure to dilute proflavine does not increase the risk of cervical precancer and cancer.
-
 Diagnosing cervical neoplasia in rural Brazil using a mobile van equipped with in vivo microscopy: A cluster-randomized community trialHunt, Brady, Fregnani, José Humberto Tavares Guerreiro, Schwarz, Richard A, Pantano, Naitielle, Tesoni, Suelen, Possati-Resende, Júlio César, Antoniazzi, Marcio, Oliveira Fonseca, Bruno, Macêdo Matsushita, Graziela, Scapulatempo-Neto, Cristovam, and others,Cancer Prevention Research 2018
Diagnosing cervical neoplasia in rural Brazil using a mobile van equipped with in vivo microscopy: A cluster-randomized community trialHunt, Brady, Fregnani, José Humberto Tavares Guerreiro, Schwarz, Richard A, Pantano, Naitielle, Tesoni, Suelen, Possati-Resende, Júlio César, Antoniazzi, Marcio, Oliveira Fonseca, Bruno, Macêdo Matsushita, Graziela, Scapulatempo-Neto, Cristovam, and others,Cancer Prevention Research 2018Cervical cancer is a leading cause of death in underserved areas of Brazil. This prospective randomized trial involved 200 women in southern/central Brazil with abnormal Papanicolaou tests. Participants were randomized by geographic cluster and referred for diagnostic evaluation either at a mobile van upon its scheduled visit to their local community, or at a central hospital. Participants in both arms underwent colposcopy, in vivo microscopy, and cervical biopsies. We compared rates of diagnostic follow-up completion between study arms, and also evaluated the diagnostic performance of in vivo microscopy compared with colposcopy. There was a 23% absolute and 37% relative increase in diagnostic follow-up completion rates for patients referred to the mobile van (102/117, 87%) compared with the central hospital (53/83, 64%; P = 0.0001; risk ratio = 1.37, 95% CI, 1.14–1.63). In 229 cervical sites in 144 patients, colposcopic examination identified sites diagnosed as cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade 2 or more severe (CIN2+; 85 sites) with a sensitivity of 94% (95% CI, 87%–98%) and specificity of 50% (95% CI, 42%–58%). In vivo microscopy with real-time automated image analysis identified CIN2+ with a sensitivity of 92% (95% CI, 84%–97%) and specificity of 48% (95% CI, 40%–56%). Women referred to the mobile van were more likely to complete their diagnostic follow-up compared with those referred to a central hospital, without compromise in clinical care. In vivo microscopy in a mobile van provides automated diagnostic imaging with sensitivity and specificity similar to colposcopy.
2017
-
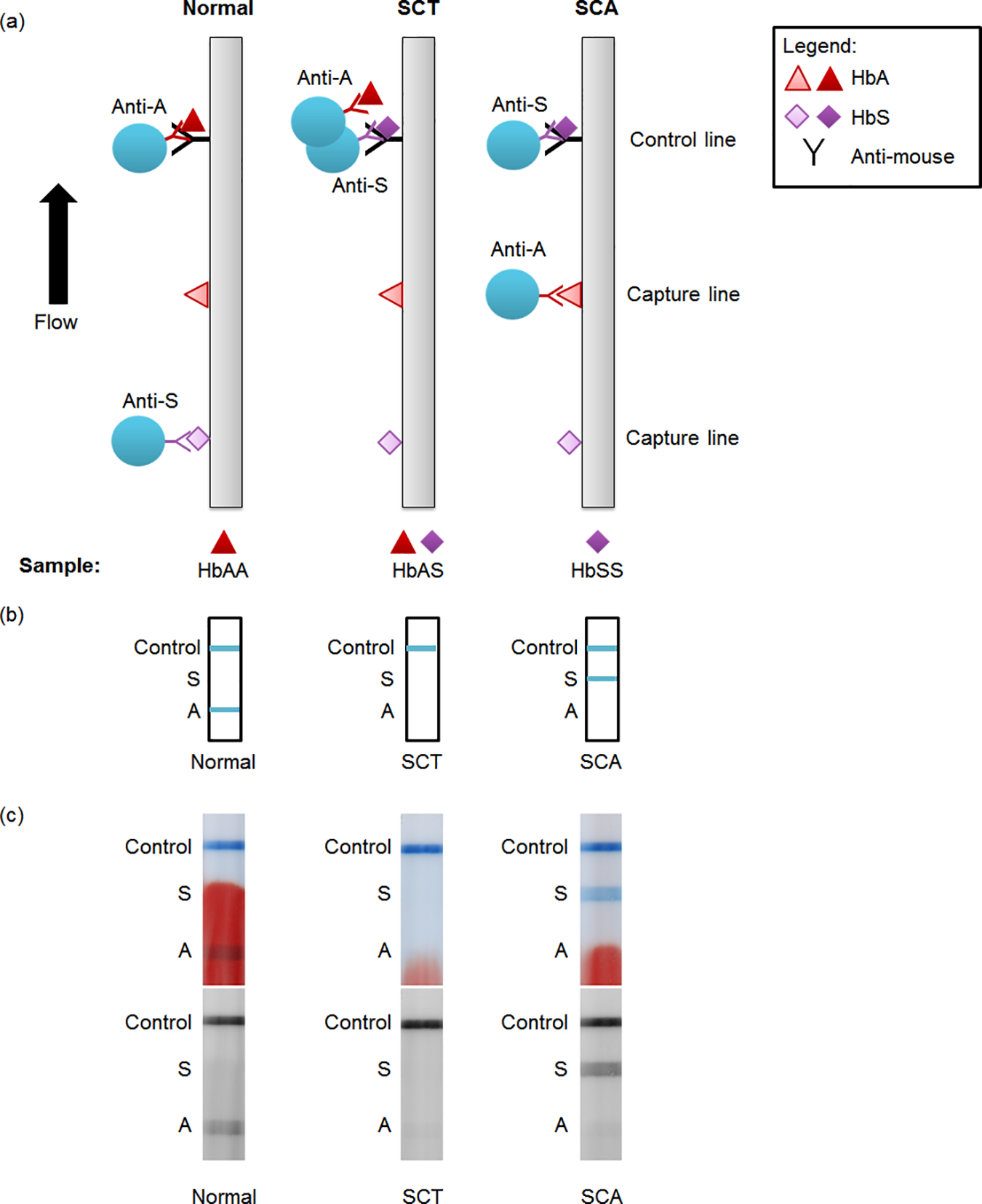 Towards a point-of-care strip test to diagnose sickle cell anemiaBond, Meaghan, Hunt, Brady, Flynn, Bailey, Huhtinen, Petri, Ware, Russell, and Richards-Kortum, RebeccaPloS one 2017
Towards a point-of-care strip test to diagnose sickle cell anemiaBond, Meaghan, Hunt, Brady, Flynn, Bailey, Huhtinen, Petri, Ware, Russell, and Richards-Kortum, RebeccaPloS one 2017A rapid test to identify patients with sickle cell disease could have important benefits in low-resource settings. Sickle cell anemia (SCA) affects about 300,000 newborns each year, the majority of whom are born in sub-Saharan Africa. Low-cost therapies are available to treat SCA, but most countries in sub-Saharan Africa lack robust neonatal screening programs needed to identify patients in need of treatment. To address this need, we developed and evaluated a competitive lateral flow assay that identifies patients with SCA (genotype HbSS) in 15 minutes using undiluted whole blood. A small volume of blood (0.5 μL– 3 μL) is mixed with antibody-coated blue latex beads in a tube and applied to the strip. Strips are then placed in a well of running buffer and allowed to run for 10 minutes. Laboratory evaluation with samples containing different proportions of hemoglobin A (HbA) and hemoglobin S (HbS) indicated that the test should enable identification of SCA patients but not persons with sickle cell trait (SCT). We evaluated the test using 41 samples from individuals with SCA, SCT, and normal blood. With visual inspection or quantitative analysis, we found a 98% accuracy when differentiating SCA from normal and SCT samples as a group (90% sensitivity and 100% specificity for identifying SCA). This work demonstrates important steps towards making a lateral flow test for hemoglobinopathies more appropriate for point-of-care use; further work is needed before the test is appropriate for clinical use.
-
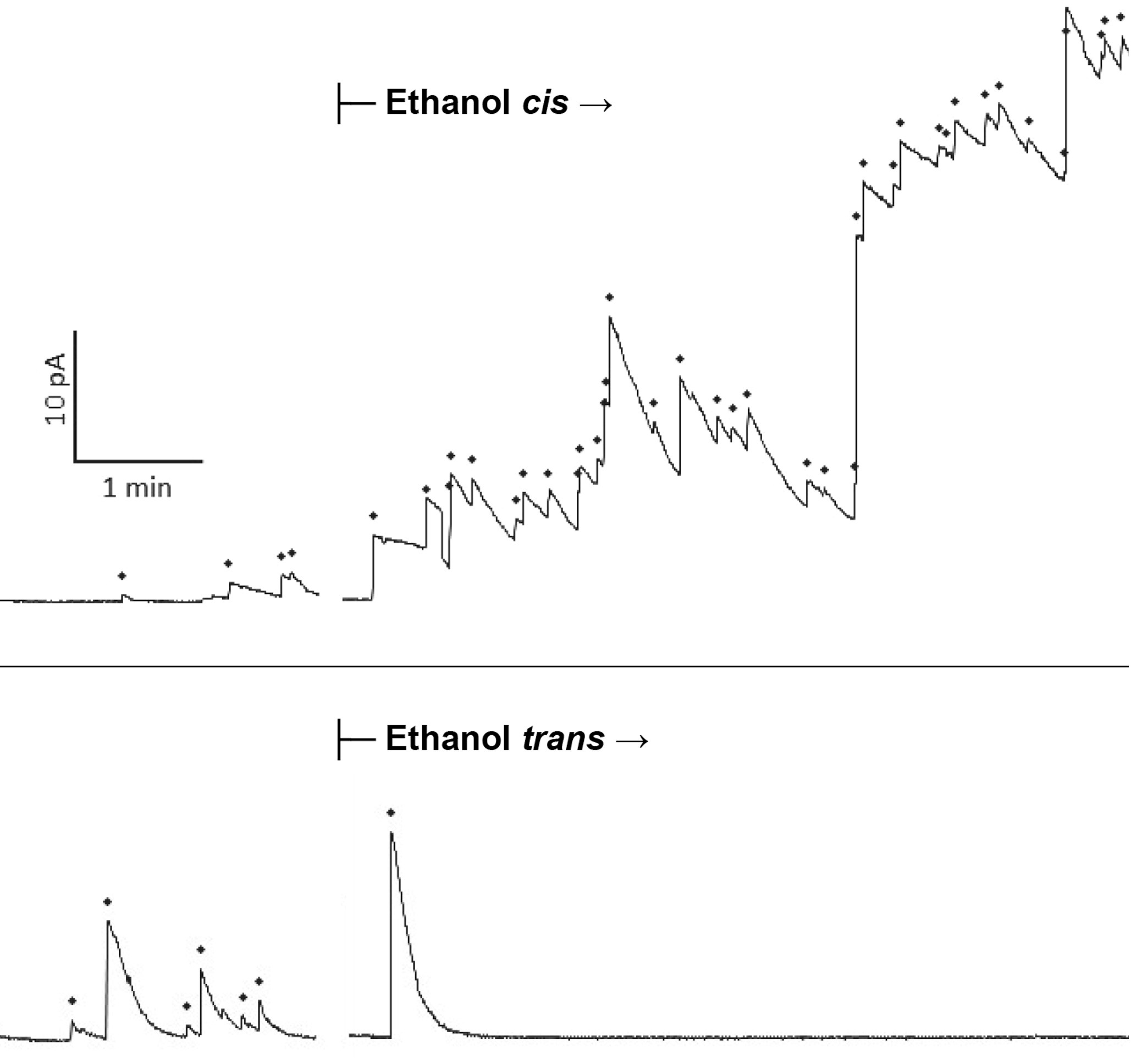 Drunken membranes: Short-chain alcohols alter fusion of liposomes to planar lipid bilayersPaxman, Jason, Hunt, Brady, Hallan, David, Zarbock, Samuel R, and Woodbury, Dixon JBiophysical journal 2017
Drunken membranes: Short-chain alcohols alter fusion of liposomes to planar lipid bilayersPaxman, Jason, Hunt, Brady, Hallan, David, Zarbock, Samuel R, and Woodbury, Dixon JBiophysical journal 2017Although the effects of ethanol on protein receptors and lipid membranes have been studied extensively, ethanol’s effect on vesicles fusing to lipid bilayers is not known. To determine the effect of alcohols on fusion rates, we utilized the nystatin/ergosterol fusion assay to measure fusion of liposomes to a planar lipid bilayer (BLM). The addition of ethanol excited fusion when applied on the cis (vesicle) side, and inhibited fusion on the trans side. Other short-chain alcohols followed a similar pattern. In general, the inhibitory effect of alcohols (trans) occurs at lower doses than the excitatory (cis) effect, with a decrease of 29% in fusion rates at the legal driving limit of 0.08% (w/v) ethanol (IC50 = 0.2% v/v, 34 mM). Similar inhibitory effects were observed with methanol, propanol, and butanol, with ethanol being the most potent. Significant variability was observed with different alcohols when applied to the cis side. Ethanol and propanol enhanced fusion, butanol also enhanced fusion but was less potent, and low doses of methanol mildly inhibited fusion. The inhibition by trans addition of alcohols implies that they alter the planar membrane structure and thereby increase the activation energy required for fusion, likely through an increase in membrane fluidity. The cis data are likely a combination of the above effect and a proportionally greater lowering of the vesicle lysis tension and hydration repulsive pressure that combine to enhance fusion. Alternate hypotheses are also discussed. The inhibitory effect of ethanol on liposome-membrane fusion is large enough to provide a possible biophysical explanation of compromised neuronal behavior.